Window installations in educational buildings, such as schools, universities, and training centers, face unique challenges. The need to ensure safety, energy efficiency, and durability, combined with cost constraints, makes these projects complex. Addressing these challenges effectively can greatly impact the comfort and functionality of classrooms, libraries, and other learning spaces. In this article, we explore some of the most common challenges in installing windows in educational buildings and discuss solutions that help create better learning environments.

1. Ensuring Student Safety and Security
Safety is a top priority in educational settings. Windows in schools must meet stringent security standards to prevent accidents and unauthorized access. Typical challenges include:
- Impact Resistance: Windows should be impact-resistant to prevent injuries in case of breakage.
- Anti-Tamper Design: Windows must prevent tampering, ensuring they can’t be opened beyond safe limits by students.
- Child-Safe Materials: The materials used for window frames and finishes must be non-toxic and free from hazardous substances.
Solution: Installing shatterproof, laminated glass and reinforced window frames can enhance safety. Additionally, safety locks and anti-tamper mechanisms are essential to prevent accidents and unauthorized access.
2. Balancing Natural Light and Temperature Control
Classrooms need ample natural light to create a welcoming and productive environment. However, large windows can sometimes lead to issues like glare and temperature imbalance, which can disrupt the learning process. Common challenges include:
- Managing Glare: Glare can make it difficult for students and teachers to see screens, boards, and other instructional materials.
- Temperature Control: Poor insulation can lead to overheating or excessive cold, making it hard to maintain a comfortable environment.
Solution: Low-emissivity (Low-E) glass can reduce glare while allowing natural light. Additionally, double-glazed windows and the use of window treatments, such as blinds or tinted films, can help maintain temperature control and reduce energy costs.
3. Addressing Acoustic Needs
Noise pollution is a significant concern in many educational facilities. Windows are one of the main points where outside noise can enter, disrupting the focus and learning environment inside. Some challenges include:
- External Noise: Schools in urban areas or near busy streets often face noise from traffic, construction, and other external sources.
- Classroom Sound Management: Poor window acoustics can make it difficult to control sound within the classroom, impacting communication between students and teachers.
Solution: Installing double or triple-glazed windows with soundproofing features can help reduce noise infiltration. These options can create a quieter, more focused environment for students, improving concentration and learning outcomes.

4. Meeting Energy Efficiency Standards
Educational buildings often have tight budgets, and energy efficiency can help reduce operational costs. However, achieving energy efficiency in window installations can be challenging due to:
- High Initial Costs: Energy-efficient windows, such as double-glazed or Low-E glass options, can be costly upfront.
- Compliance with Standards: Windows must meet local energy codes, which may require specialized materials and installation techniques.
Solution: Schools can benefit from grants or incentives for energy-efficient renovations, which can help offset the costs of high-quality window installations. Working with experienced contractors who specialize in educational buildings can also ensure that installations meet energy efficiency standards without compromising on quality.
5. Choosing Durable Materials Suitable for High Traffic Areas
Educational buildings are high-traffic environments, and windows must withstand regular use and occasional rough handling. Some durability-related challenges include:
- Wear and Tear: Frequent use can lead to wear, especially in areas where windows are regularly opened for ventilation.
- Vandalism: Unfortunately, educational facilities can sometimes experience vandalism, requiring more robust materials to avoid frequent replacements.
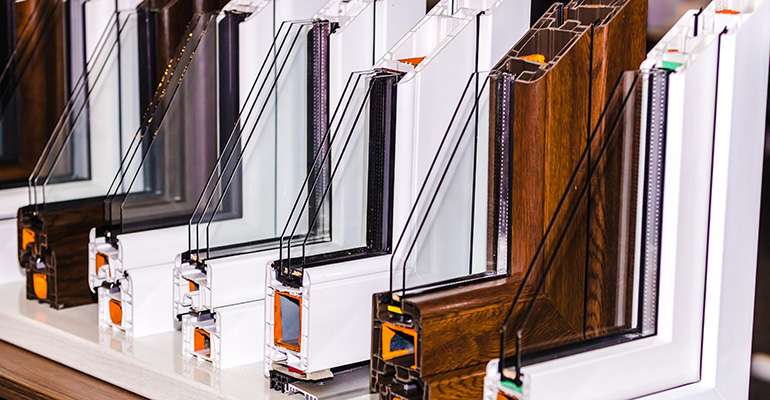

Solution: High-quality materials, such as reinforced aluminum or vinyl frames, provide durability and low maintenance. Laminated glass can also be a suitable option for areas prone to vandalism, as it is harder to break and maintains integrity even if damaged.
Conclusion
Installing windows in educational buildings comes with a unique set of challenges, from ensuring student safety and controlling temperatures to managing noise and meeting energy efficiency standards. By choosing the right materials and designs, educational institutions can create safe, comfortable, and productive environments that promote learning and well-being. With proper planning and the use of specialized solutions, window installations can enhance both the functionality and aesthetics of educational spaces, benefiting students and staff alike.


